While tinnitus is a symptom rather than a disease in itself, it’s frequently associated with hearing loss. This relationship is complex and bidirectional. On one hand, hearing loss can lead to tinnitus. When our ability to hear external sounds diminishes, our brain sometimes compensates by ‘filling in the gaps’ with its own noises, leading to tinnitus. This is particularly common in cases of age-related or noise-induced hearing loss.
On the other hand, the presence of tinnitus can also exacerbate the challenges of hearing loss. Tinnitus can mask or distract from external sounds, making it harder for individuals to focus on real auditory inputs, thereby intensifying the practical and emotional impacts of hearing impairment. Understanding this intricate relationship is key to managing both conditions effectively.
How Damage to the Ear Leads to Tinnitus and Hearing Loss
The ear is a complex organ, and damage to any part of it can lead to hearing problems. The most common point of damage is the cochlea, where tiny hair cells detect sound waves and translate them into nerve signals. When these hair cells are damaged or destroyed – due to factors like loud noise, aging, or disease – they can’t be repaired. This leads to a reduction in the quality or quantity of signals sent to the brain, resulting in hearing loss.
Simultaneously this damage can lead to tinnitus. The brain, used to receiving regular signals from the auditory nerve, may start to ‘fill in’ the missing input by generating its own noises, leading to the perception of sound where there is none. This phenomenon is akin to ‘phantom limb’ sensations experienced by amputees.
Understanding these connections helps in recognising the importance of early intervention and treatment to mitigate the effects of both tinnitus and hearing loss. By tackling the root causes, we can better manage these conditions and improve the overall quality of life for those affected.
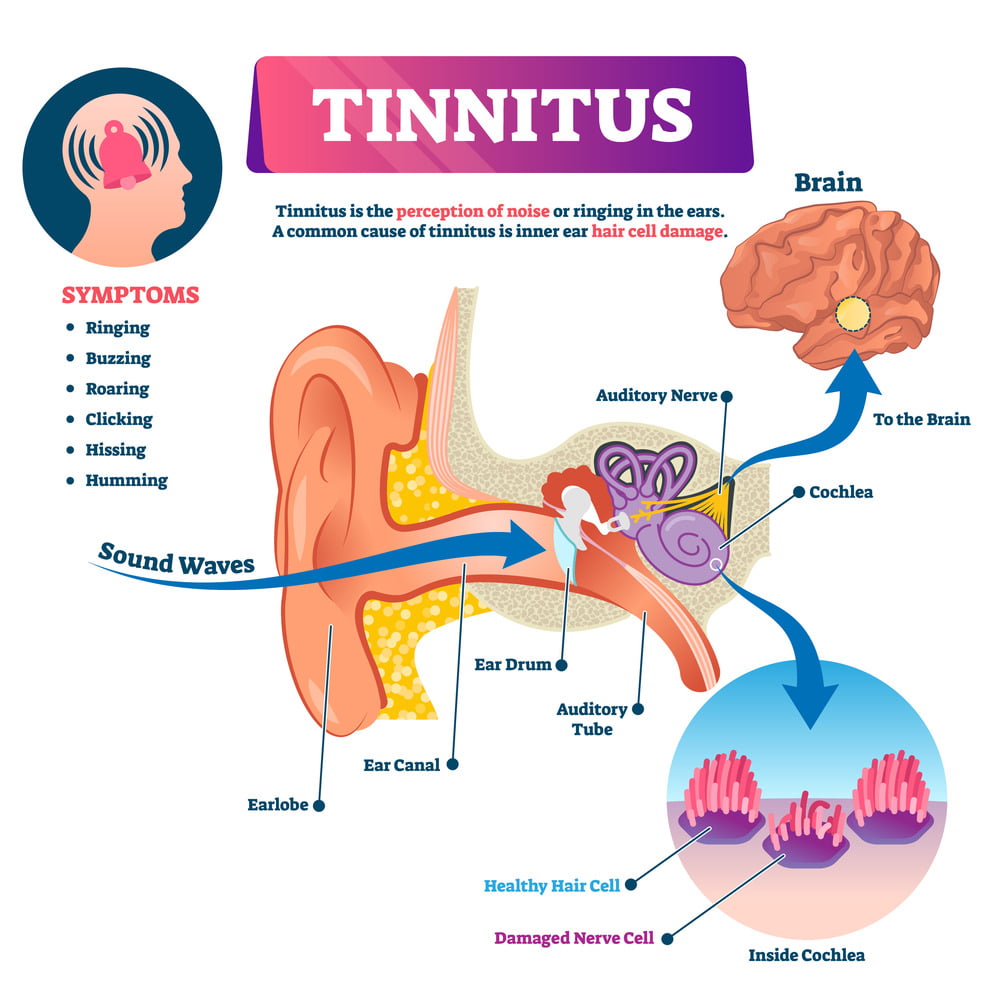
Causes of Tinnitus and Their Connection to Hearing Loss
- Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis): One of the most common causes of hearing loss is the natural aging process. As we age, the delicate hair cells in our inner ear may deteriorate or become damaged, leading to hearing loss. This same damage can trigger tinnitus, as the brain tries to compensate for the loss of auditory input.
- Exposure to Loud Noise: Prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause noise-induced hearing loss and is also a leading cause of tinnitus. This can happen gradually over time or suddenly, such as after a loud concert. The noise damages the hair cells in the cochlea, disrupting normal auditory processing.
- Ear Blockages: Blockages due to earwax build-up, infections, or benign tumours can cause both hearing loss and tinnitus. These blockages alter the way sound is conducted through the ear, potentially leading to tinnitus.
- Ototoxic Medications: Certain medications can be harmful to the auditory system, leading to tinnitus and hearing loss. These include some antibiotics, cancer medications, and large quantities of aspirin.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like Meniere’s disease, which affects the inner ear, can lead to tinnitus and hearing loss. Other medical issues, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, can also play a role.
Impact on Daily Life
Tinnitus and hearing loss significantly impact daily life, affecting communication, mental health, professional performance, and overall wellbeing.
- Communication Challenges: Difficulties in understanding speech, particularly in noisy environments, can lead to misunderstandings and strained relationships. Furthermore, the frustration of communication barriers often results in social withdrawal and isolation.
- Mental Health Impacts: The persistent nature of tinnitus can cause stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. There’s an increased risk of depression due to the chronic challenges associated with these conditions.
- Professional Life: Hearing loss and tinnitus can hinder job performance, especially in roles requiring sharp auditory skills. These conditions may also limit career advancement in professions reliant on precise hearing.
- Cognitive Load: The effort to hear and interpret sounds can be mentally taxing, reducing cognitive resources for other tasks.

The Role of Hearing Aids and Accessories
Hearing aids and specialised accessories play a vital role in managing the symptoms of both hearing loss and tinnitus, enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
Hearing aids compensate for hearing loss by amplifying external sounds, making it easier to hear conversations and ambient noises. Additionally, many modern hearing aids come with tinnitus masking features. They produce a sound that can help distract the user from the tinnitus, reducing its perceived intensity. By improving overall hearing, these devices can reduce the cognitive strain and social isolation often associated with hearing loss and tinnitus.
Furthermore, through integrating specialised accessories with their hearing aids, individuals with tinnitus and hearing loss can experience significant symptom relief. Some helpful accessories include:
- Sound Pillows: These are specially designed pillows with built-in speakers. They allow individuals with tinnitus to listen to soothing sounds or white noise at bedtime, which can mask tinnitus sounds and aid in better sleep.
- Specialised Tinnitus Headphones: These headphones are tailored for people with tinnitus. They can be used for sound therapy, an effective method of tinnitus management that involves listening to specific types of sounds to reduce the prominence of tinnitus.
- Sound Therapy Machines: These devices offer a variety of sounds like white noise, nature sounds, or music, which can provide relief by masking the tinnitus. They are particularly useful during quiet times when tinnitus symptoms can feel more pronounced.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while tinnitus and hearing loss present significant challenges, the right tools and strategies can greatly alleviate their impact. At Hearing Aid Accessories, we understand these challenges and are committed to providing solutions that enhance the quality of life for those affected.
We offer a carefully curated selection of products designed specifically to aid individuals with tinnitus. From sound therapy machines that offer a soothing auditory experience to specialized tinnitus headphones and sound pillows for better sleep, our range caters to the diverse needs of our customers.
We invite you to browse our collection and discover how our products can bring you relief and improve your daily living.