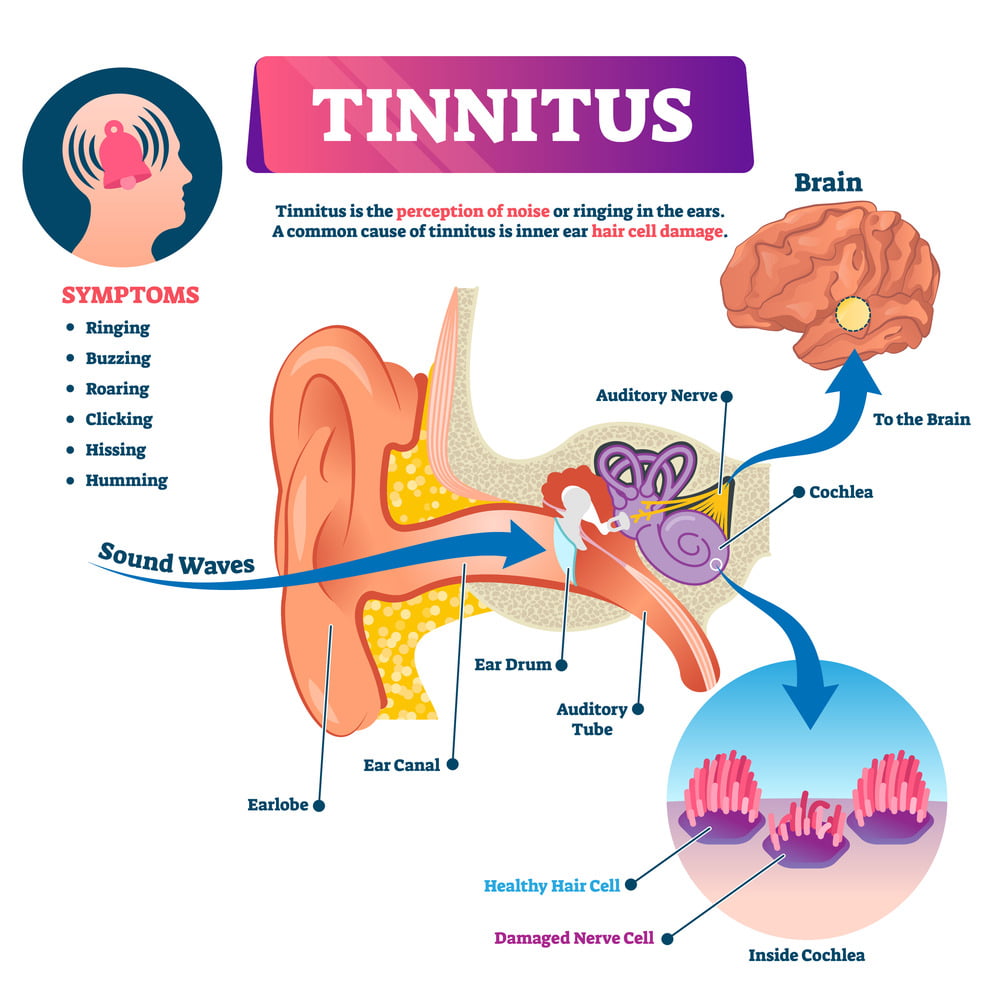
Tinnitus, characterised by a persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears, affects millions worldwide. Yet, despite its prevalence, numerous myths and misconceptions surround this condition. At Hearing Aid Accessories, we believe knowledge is empowerment. So, let’s set the record straight by debunking some common tinnitus myths.
Tinnitus Myth 1: It is a Disease
Truth: Many people mistakenly believe tinnitus to be a standalone disease. However, tinnitus is more accurately described as a symptom or an indicator of something else happening within the auditory system or other parts of the body. Some common causes include:
- Age-Related Hearing Decline
- Earwax Blockage
- Loud Noise Exposure
Tinnitus Myth 2: Only Loud Noise Exposure Causes It
Truth: Tinnitus is often associated with exposure to loud noises, but it’s only one of the many potential triggers. A deeper understanding reveals:
- Medications: Some medications have tinnitus as a potential side effect. These can range from specific antibiotics and diuretics to high doses of aspirin.
- Infections: Ear infections can temporarily cause tinnitus. If left untreated, the tinnitus might persist even after the infection has cleared.
- Head or Neck Injuries: Traumatic injuries, especially those affecting the inner ear or causing nerve damage, can result in tinnitus.
- Certain Illnesses: Diseases such as Meniere’s disease, which involves fluid buildup in the inner ear, or conditions affecting the blood vessels can lead to tinnitus.
Thus, while loud noises are a common cause, tinnitus has a broader range of potential triggers, emphasising the importance of comprehensive medical evaluations.
Tinnitus Myth 3: It is Always Permanent
Truth: The idea that once tinnitus starts, it’s forever can be quite daunting. Fortunately, this isn’t always the case:
- Short-Term Triggers: Events like attending a loud concert or being in an environment with high noise levels can lead to temporary tinnitus. The ringing or buzzing might last for a few hours to a couple of days before fading away.
- Health-Related Causes: Simple health issues, such as a cold or an ear infection, can sometimes cause tinnitus. As the health condition improves, the tinnitus typically resolves.
- Importance of Evaluation: While many instances of tinnitus are temporary, it’s crucial not to ignore persistent symptoms. If your tinnitus continues beyond a week or frequently reoccurs, it’s advisable to consult with an audiologist or an ear, nose, and throat specialist. They can help pinpoint the cause and provide guidance on potential treatments.
Tinnitus Myth 4: Hearing Aids Won't Help
Truth: The idea that hearing aids are only for improving hearing and won’t assist with tinnitus is a common misconception. Modern advancements in hearing aid technology provide hope for those grappling with tinnitus.
Many of today’s hearing aids have integrated tinnitus maskers. These maskers produce a soft sound, like white noise or nature sounds, which can help divert the brain’s attention away from the constant ringing or buzzing of tinnitus.
Furthermore, by amplifying ambient sounds, hearing aids can make tinnitus less noticeable. When background sounds are more pronounced, the contrast between them and the tinnitus can decrease, making the latter less bothersome.
Hearing professionals can adjust hearing aids to cater to individual needs. This means the tinnitus masking sound can be personalised to provide optimal relief for each user.

Tinnitus Myth 5: It Only Affects the Elderly
Truth: Age can be a factor in many health conditions, and while the elderly might report tinnitus more frequently, it’s incorrect to assume that they are the only age group affected. Tinnitus doesn’t discriminate by age. From teenagers exposed to loud music to young adults facing stress or certain medical conditions, tinnitus can manifest at any life stage.
Moreover, children, often assumed to be immune from such conditions, can also experience tinnitus. Causes in children can range from exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or even the result of certain medications.
Tinnitus Myth 6: Nothing Can Be Done About It
Truth: Feeling helpless is a common emotion among those with persistent tinnitus. The misconception that there’s no solution can be distressing, but in reality, various therapeutic avenues are available:
- Sound Therapy: This approach uses external noise to counteract the perception of tinnitus. It can be as simple as using a white noise machine at night or more specialised equipment like tinnitus maskers integrated into hearing aids.
- Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy (CBT): Tinnitus can be mentally and emotionally taxing. CBT helps individuals change their negative reactions to tinnitus, teaching coping strategies and altering the way they perceive the condition.
- Medications: While no drug is approved to treat tinnitus specifically, some medications can help reduce its severity or alleviate the stress and anxiety associated with it. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider about potential pharmaceutical options.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding certain triggers, managing stress, and limiting exposure to loud noises can help in reducing the frequency or severity of tinnitus episodes.
While it’s true that a one-size-fits-all cure for tinnitus remains elusive, the above treatments have offered countless individuals relief and improved quality of life.
In Conclusion
Now that you have learnt about tinnitus myth. It can be a challenging condition, but with the right knowledge, support, and tools, it’s manageable. Always rely on credible sources and professionals for guidance.
For those affected by tinnitus, Hearing Aid Accessories offers a wide range of products designed to alleviate its symptoms. We invite you to browse our collection and discover innovative solutions that can enhance your auditory experience and provide the relief you deserve.

