Healthy teeth and dental hygiene are essential for a bright, radiant smile. But did you know that your dental health also affect your hearing system? Many people are unaware that proper dental hygiene is essential for their ability to hear well. To understand the connection between the two, we must first explore the process of hearing itself.
How Does Hearing Work?
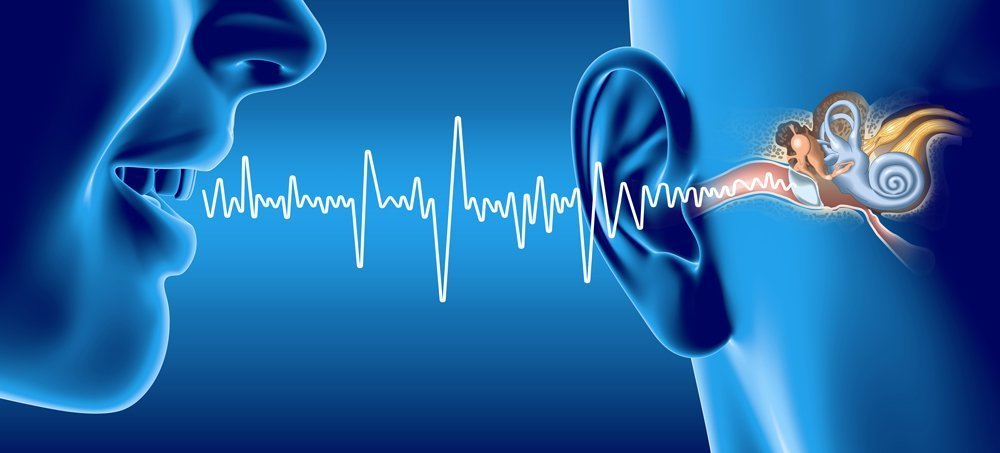
Hearing begins with the outer ear: it collects sound waves, which then enter the ear canal and reach the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. The eardrum sends the vibrations into the middle ear. These vibrations then travel to the inner ear, where the cochlea (a snail-shaped structure filled with fluid) is located.
Once the sound waves reach it, they begin to stimulate the stereocilia: the tiny hair cells inside the inner ear which translate sound waves into electrical impulses and send them to the brain for interpretation via the auditory nerve.

Oral Bacteria - Dental Hygiene
Neglecting your oral hygiene by not brushing or flossing your teeth correctly can lead to an array of dental hygiene issues such as periodontal disease, infections, and abscesses. All of these can cause harmful bacteria to proliferate and eventually- enter the bloodstream, resulting in inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels. These include the blood vessels responsible for hearing.
When proper blood circulation to the hair cells inside the cochlea is disrupted, they can become damaged, or even permanently destroyed, leading to hearing loss.
Wisdom Teeth
When molars grow, they can cause pain, headaches, and earaches. Impacted wisdom teeth can lead to infections, and subsequently- inflammation. Similarly to the effects caused by harmful bacteria, wisdom teeth inflammation can narrow the blood vessels and disrupt the blood flow to the hair cells inside the cochlea, harming your ability to hear well.
So, while wisdom teeth themselves cannot cause hearing loss, if they do become infected, they can increase your risk of inflammation, poorer dental hygiene and hearing problems.
TMJ Disorder
TMJ disorder (or temporomandibular joint disorder) is a condition that relates to the way in which the jaw moves. The mandible is the jaw, and the temporomandibular joint connects the jaw to the skull. TMJ disorder occurs when there is a chronic or acute inflammation of the joint and can be extremely painful, making eating and speaking difficult.
The disorder can trigger a specific form of hearing loss called TMJ hearing loss, once again occurring due to inflammation and poor dental hygiene. Furthermore, the nerve pain signals can reach the inner ear nerve pathway, causing the ear to react to the pain by contracting the muscles. Frequent contraction of these muscles can interfere with the natural opening and closing of the Eustachian tube, leading to a build-up of pressure within the ear.
Fortunately, TMJ hearing loss is typically temporary, and TMJ disorder can usually be treated by your dentist or a TMJ specialist.

Protecting Your Hearing from Dental Hygiene-Related Damage
Having a proper dental hygiene routine is essential to preventing bacteria build-up that could lead to inflammation and damage your hearing health. Make sure to brush your teeth twice a day and floss at least once. In case you’ve been suffering from TMJ, you should seek advice from your local dental professional.
What If Hearing Loss Has Already Occurred?
In case you think you might already be suffering from hearing loss (dental hygiene -related or not), early diagnosis and intervention are of great importance. The most suitable treatment will depend on your specific type and level of hearing loss.
Do you feel like you haven’t been hearing as well as you should? Why not book a free hearing test with our sister company Hear4U? Our experienced audiologists will assist you with any questions you may have and will help you determine the most appropriate treatment. Click to book your appointment and shop for hearing aid accessories here!